 Image credit: Adrian Salavaty
Image credit: Adrian SalavatyAbstract
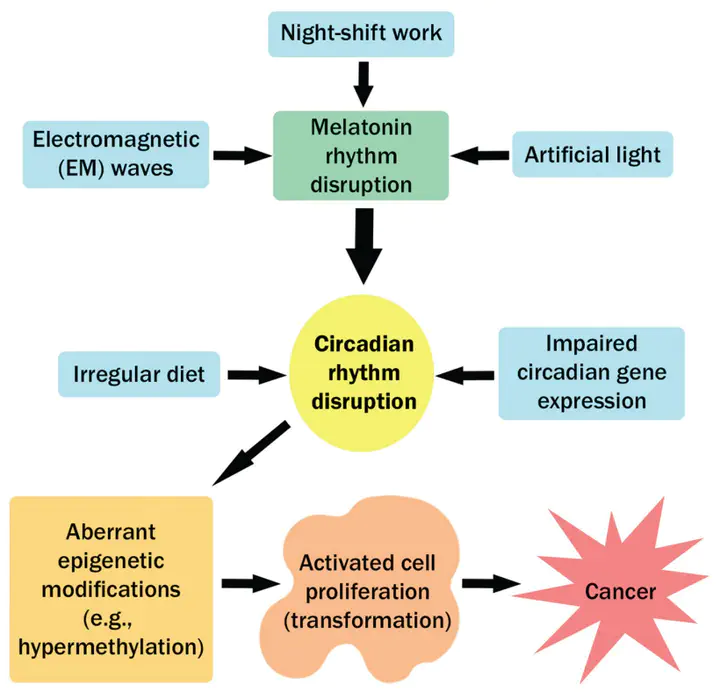
Circadian rhythms refer to the endogenous rhythms that are generated to synchronize physiology and behavior with 24-h environmental cues. These rhythms are regulated by both external cues and molecular clock mechanisms in almost all cells. Disruption of circadian rhythms, which is called circadian disruption, affects many biological processes within the body and results in different long-term diseases, including cancer. Circadian regulatory pathways result in rhythmic epigenetic modifications and the formation of circadian epigenomes. Aberrant epigenetic modifications, such as hypermethylation, due to circadian disruption may be involved in the transformation of normal cells into cancer cells. Several studies have indicated an epigenetic basis for the carcinogenic effects of circadian disruption. In this review, I first discuss some of the circadian genes and regulatory proteins. Then, I summarize the current evidence related to the epigenetic modifications that result in circadian disruption. In addition, I explain the carcinogenic effects of circadian disruption and highlight its potential role in different human cancers using an epigenetic viewpoint. Finally, the importance of chronotherapy in cancer treatment is highlighted.
Key words
Cancer, Epigenetics, Circadian rhythms, Circadian disruption, Chronotherapy
Click the Cite button above to import the publication metadata into your reference management software.